What is Fuel Economy? OR Simply, How much it gives?
Fuel economy: The Myth and The Reality
Fuel economy is one of the most sensitive issues and an important factor while buying an automobile; be it a motorcycle, a car or even a truck or bus. For most automotive buyers across the world, it affects the running expenses of the vehicle. In simple terms, fuel economy is the number of kilometers per liter or gallon worth of fuel.
A car’s mileage or average is the number of kilometers or miles it travels on a liter or a gallon of fuel as the case may be. However, in the real world scenario, the fuel economy of a vehicle is calculated based on the number of kilometers traveled on a full tank of fuel. For e.g. 15.0 Km/L for a car or 60 Km/L for a bike on an average.
But, in some European countries; this is reversed. There, the fuel economy is measured in terms of the number of liters of fuel consumed per 100 kilometers for e.g. 8 liters/100 Km in case of a car or 2.5L/100 Km in case of a motorcycle on an average.

Who certifies the Fuel Economy data?
Every country has its own standards and testing agency to test fuel economy. In America, the United States Environment Protection Agency (US-EPA) certifies this by conducting tests which measure the total volume of carbon captured from the vehicle’s exhaust. All vehicle manufacturers are required by law to display the fuel economy ratings on the cars sold in the USA. In the US, fuel economy is measured in ‘Miles per Gallon’ or mpg.

In India, Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI) conducts fuel economy tests based on Indian Driving Cycle (IDC). Indian Driving Cycle (IDC) is a laboratory test conducted on a rolling road which simulates a typical Indian driving environment over 10 kilometers. However, in the real world driving conditions, you can expect to get -10% to -20% (less) of the ARAI certified values as claimed by manufacturers.
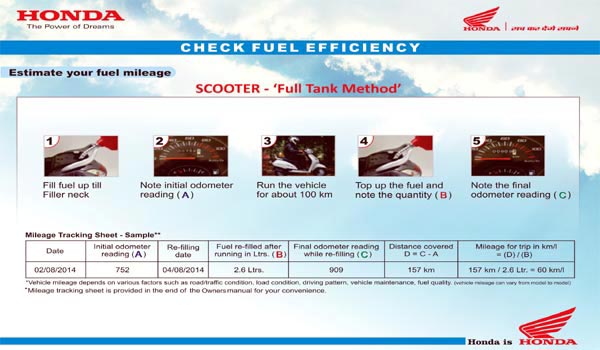
How to calculate your car’s mileage/fuel economy? Full-Tank Method:
Fuel economy can be calculated by the formula: Distance traveled ÷ Fuel used
For e.g. – A car travels 300 km on 20 liters of fuel, then the car’s mileage can be said to be
= 300 km ÷ 20 L = 15 Km/L
Similarly,
If a car consumes 20 liters of fuel to travel a distance of 300 km, then the car’s mileage can be said to be = [(100 km X 20 Litres) ÷ 300] = 6.66 L/Kms.
Thus, the car’s mileage would be 6.66 Litres / 100 Km.
In both cases, you must fill the tank to the fullest and set the trip-meter to ‘0’. Then after traveling at-least 100 kilometers, again refill the tank to determine the fuel average correctly. Here, you will have to also make sure that the tank is full when refilled. Repeat this exercise 3-4 times to get the mean/average result. However, this method can be erroneous as one cannot correctly determine whether that tank is really full or not. As a result, this method can give an error in the calculation of upto +/- 1 to 3%.
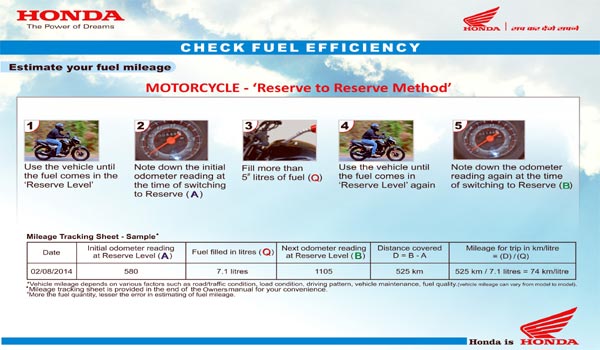
How to calculate your bike’s average/fuel economy? Reserve Method:
Most Indian bikes have a ‘reserve’ tap which uses reserve fuel when the bike’s fuel tank runs out of its main storage. When you get to reserve and turn the tap to the reserve position, just note the odometer reading (Say 15,000 km). Then, fill the tank with say 3 liters of fuel. Now, ride the bike until it again reaches the reserve point. As soon as it comes to the reserve, note down the odometer reading again (Say 15,200 km). Now subtract the earlier odometer reading from the new one. Assuming that your bike traveled, say, 200 kilometers after it reached the reserve position, then its fuel economy is = Kilometres covered / Number of liters of fuel consumed which is
= 200 km ÷ 3 Litres = 66.66 Km/L
This simply means, your bike is giving a fuel economy of 66.66 Km/L. Repeat this exercise 3-4 times to get the mean/average result. This is a more reliable method as it reduces the possibility of error in calculation.
How to calculate your vehicle’s mileage/fuel economy? Bottle method:
The correct way to check the vehicle’s mileage is by using a 1-liter bottle. This is a special bottle of exact 1-liter capacity (usually available at dealerships).
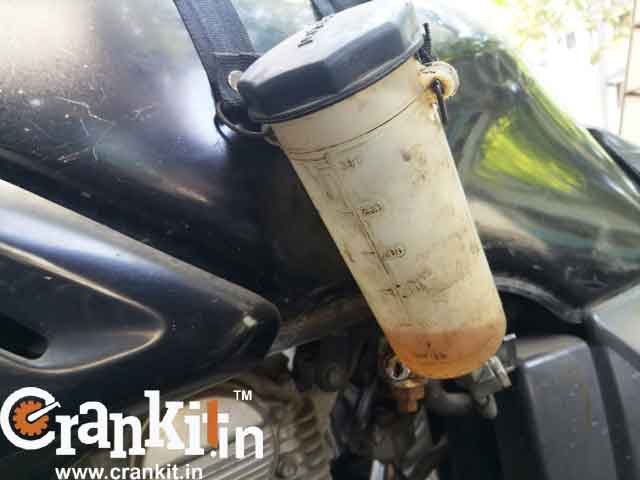

Fill the bottle with 1-liter petrol and attach the tube end to the carburetor inlet of bike or car. Set the trip-meter to ‘0’. Then, run the car or bike till the fuel in the bottle runs out or finishes. Note the reading on the trip-meter. The number of kilometers you traveled indicates your car or bike’s actual average or the fuel economy. This is most reliable of the three methods as there is no chance of error if any.
Factors that badly affect fuel economy are:
- Vehicle road-worthiness
- Engine condition
- Tire condition
- Road conditions (e.g. bad, loose gravel, icy, uphill, winding, narrow etc.)
- Stop-and-go traffic
- High speed or aggressive driving
- Cold temperatures
- AC and other accessory loads
- Number of passengers
- Amount of cargo/load
How to get the best mileage/average from your car or bike: 10 points check-list for better fuel economy
- Keep your vehicle’s engine in a healthy condition. A poorly maintained engine creates too much friction and seriously affects the fuel economy.
- Service your vehicle regularly so all the systems work at optimum temperatures and pressures. Use manufacturer recommended engine oil to get the best performance from your engine.
- Never modify your vehicle in a manner which affects its performance. Putting up parts such as crash-guards / protruding decals/visors / modified exhausts or any other unauthorized modification can reduce the aerodynamic performance of the vehicle; resulting in low fuel economy / poor mileage.
- Don’t overload the vehicle or put the cargo on the vehicle’s roof. Reduce load/weight when necessary. Keep tires inflated to recommended pressures. Low tire pressure can cause more surface friction, resulting in low fuel economy.
- Don’t idle your vehicle too much. If you stop at traffic lights, then turn off the engine as idling gives 0 Km/L. Use cruise control to save fuel.
-
Use vehicles with more advanced technologies such as start-stop systems, micro-hybrids, mild or full hybrids or i3s which saves the fuel.
- Drive safely and in the correct gear. Never rev the engine too much as doing so only burns more fuel. Don’t raise the throttle to reach the red-line, unless you are driving in a race.
- Drive steadily at the speed of 60 to 70 Km/h in the top gear to get the best fuel economy/mileage/average from your vehicle. (This translates to approx. 1400-2000 rpm for diesel engines and 1200-1800 rpm for petrol engines on a level road.) Any speed above or below this will not deliver the desired results. You must anticipate the traffic and use gears, instead of brakes, to slow down by taking the foot off the accelerator (coasting). Avoid both rapid braking and/or rapid acceleration at all costs.
- Don’t press/keep the foot on the clutch/brake pedal while driving as the clutch slips you lose the power to the wheels. Don’t use 4×4 when not needed. Driving the vehicle in 4×4 mode reduces the mileage by about 1 Km/L.
- Turn off the air conditioner or when not needed. Roll down the windows while driving at slow speeds. Since the A/c draws power from the engine and turning it on consumes more fuel. So, use A/c sparingly or instead use just the blower (especially in winters). Don’t use warmers/heaters, defrosters more than needed.
For more information, you can refer to the ARAI website.
Read on: What is horsepower? >>
